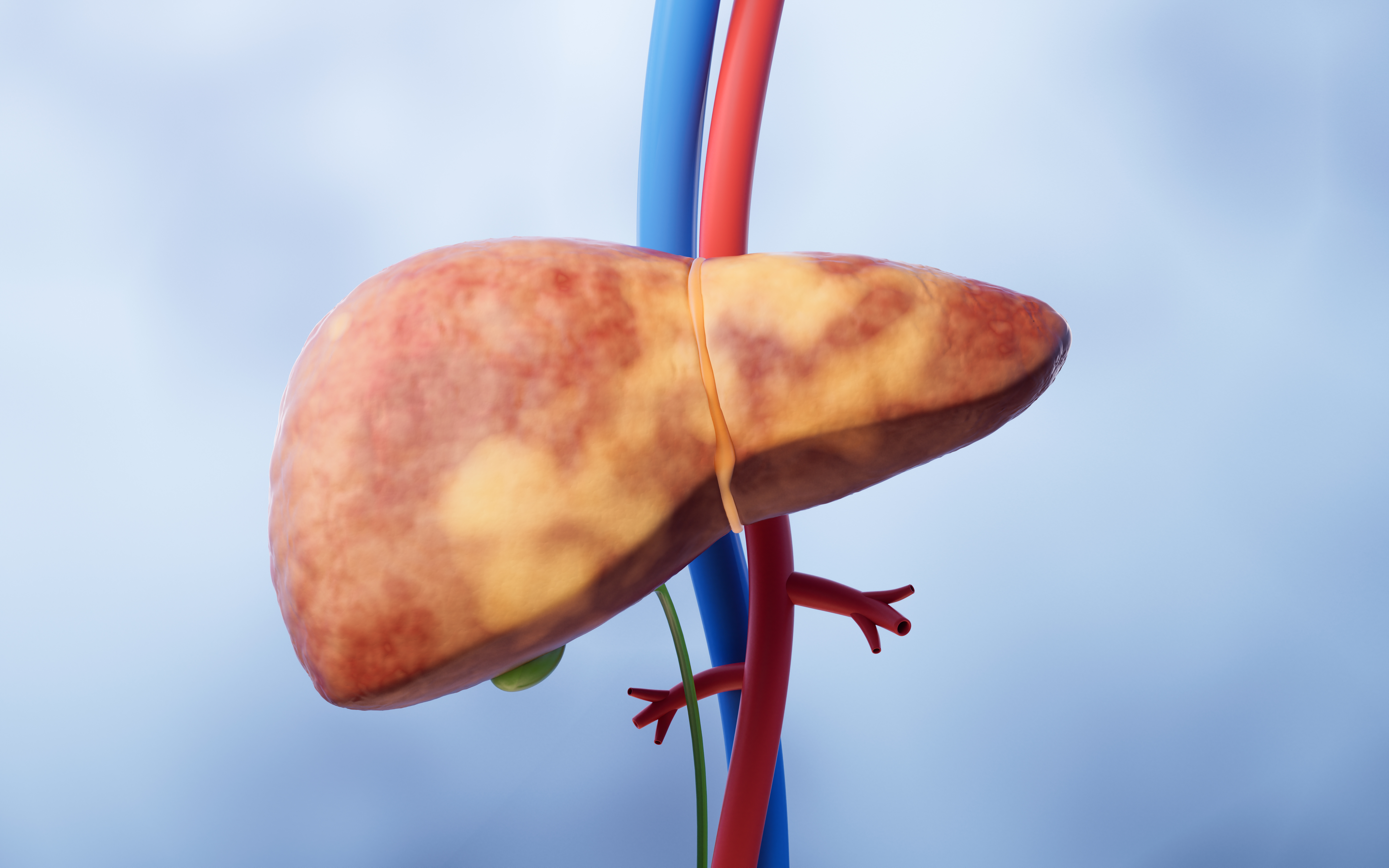
What is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver is a common health problem. It happens when too much fat builds up in the liver. This condition is also called hepatic steatosis. While some fat in the liver is normal, too much can cause health issues. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), fatty liver affects millions of people worldwide. Early detection is important because, in many cases, fatty liver does not cause symptoms at first. However, over time, it can lead to liver damage.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Most people with fatty liver do not notice any symptoms at first. Still, as the condition gets worse, some signs may appear. For example, you might feel tired more often. In addition, you may notice discomfort or pain in the upper right side of your belly. Other possible symptoms include:
However, many people do not have any symptoms until the liver is badly damaged.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are several fatty liver causes. The most common are drinking too much alcohol and being overweight. But, even people who do not drink alcohol can get fatty liver. This is called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Other risk factors include:
For some people, genetics play a role. In addition, unhealthy eating habits and lack of exercise increase the risk.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver
Doctors use several methods to diagnose fatty liver. First, they may ask about your medical history and symptoms. Next, they will do a physical exam. Blood tests can show if your liver is working well. Sometimes, doctors use imaging tests, such as:
In some cases, a liver biopsy is needed. This test checks a small piece of liver tissue for fat and damage. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends regular check-ups for people at risk.
Treatment Options
Fatty liver treatment depends on the cause and how severe it is. For most people, lifestyle changes are the main treatment. If alcohol is the cause, stopping drinking is key. For non-alcoholic fatty liver, doctors may suggest:
Sometimes, medicines are needed to treat related problems. However, there is no specific medicine for fatty liver itself. In rare cases, if the liver is very damaged, a liver transplant may be needed.
Lifestyle and Dietary Guidance
Making healthy choices can help your liver. For example, eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Choose lean proteins, such as fish or chicken. In addition, limit foods high in sugar, salt, and fat. Try to avoid processed foods and sugary drinks. Regular exercise, like walking or swimming, helps burn fat and keeps your liver healthy. Also, if you smoke, quitting can help your liver recover.
Prevention Tips
You can take steps to prevent fatty liver. Here are some tips:
By following these steps, you lower your risk of fatty liver and other health problems.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice any fatty liver symptoms, such as tiredness or belly pain, talk to your doctor. Also, if you have risk factors like diabetes or obesity, regular check-ups are important. Early treatment can prevent serious liver damage. Remember, only a doctor can diagnose and guide you on fatty liver treatment. For personalized advice on fatty liver, consult a gastroenterologist.